Getting your website to rank higher on Google isn’t just about creating great content or building backlinks. There’s a technical SEO side that works behind the scenes, making sure search engines can find, understand, and properly rank your website. This is where technical SEO comes into play.
Whether you’re running an online store, managing a business website, or maintaining a blog, understanding technical SEO is crucial for your online success. At Socio Greek, we’ve helped numerous businesses improve their search visibility through strategic technical optimization. In this technical SEO guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to get your website technically sound and ready to rank in 2026.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website’s technical elements to help search engines crawl, understand, and index your pages more effectively. Think of it as building a strong foundation for your house without it, everything else becomes unstable.
Unlike content SEO (which focuses on what you write) or off-page SEO (which deals with backlinks), technical SEO handles the structural and performance aspects of your website. It ensures that search engine bots can access your site easily, your pages load quickly, and users have a smooth experience when they visit.
In simple terms, technical SEO makes your website “search engine-friendly” by addressing things like site speed, mobile compatibility, security, site structure, and more. It’s the backbone that supports all your other SEO efforts.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
You might have the best content on the internet, but if search engines can’t properly crawl or index your website, no one will ever find it. That’s why technical SEO matters so much.
- Better Search Rankings: Search engines like Google prioritize websites that are technically optimized. If your site loads fast, works well on mobile devices, and has a clean structure, you’re more likely to rank higher than competitors who ignore these factors.
- Improved User Experience: Technical SEO isn’t just about pleasing search engines-it’s about creating a better experience for your visitors. When your site loads quickly, works smoothly, and is easy to navigate, people stay longer and engage more with your content.
- Higher Conversion Rates: A technically sound website leads to better user experiences, which directly impacts your bottom line. Studies show that even a one-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by 7%.
In 2026, with AI-powered search results and user experience metrics becoming more important than ever, technical SEO has moved from “nice to have” to absolutely essential.
What Is the Technical SEO Checklist for 2026?
Now let’s dive into the practical steps you need to take. This comprehensive technical SEO checklist covers everything you need to optimize your website for search engines and users alike.
1. Make Your Website Mobile-Friendly
More than 60% of all internet searches now happen on mobile devices. If your website doesn’t work well on smartphones and tablets, you’re losing more than half your potential visitors-and your search rankings will suffer too.
Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it looks at the mobile version of your website first when deciding how to rank you. Making your site mobile-friendly isn’t optional anymore; it’s essential.
What mobile-friendly means:
- Your website automatically adjusts to fit different screen sizes
- Text is readable without zooming in
- Buttons and links are easy to tap with a finger
- Images resize properly across devices
- No intrusive pop-ups that block content on mobile
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your website passes the mobile test and get instant feedback on what needs fixing.
2. Secure It with HTTPS

Website security is both a trust factor and a ranking signal. Google gives preference to secure websites, and visitors are more likely to trust and stay on sites that show the padlock icon in their browser.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data transferred between your website and your visitors. This protects sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, and personal data from being intercepted.
Implementation steps:
- Get an SSL certificate from your hosting provider
- Install the certificate on your server
- Update all internal links to use HTTPS
- Set up 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS
- Update your sitemap and notify Google Search Console
The padlock icon next to your URL tells visitors and search engines that your site is safe and trustworthy.
3. Work on Core Web Vitals
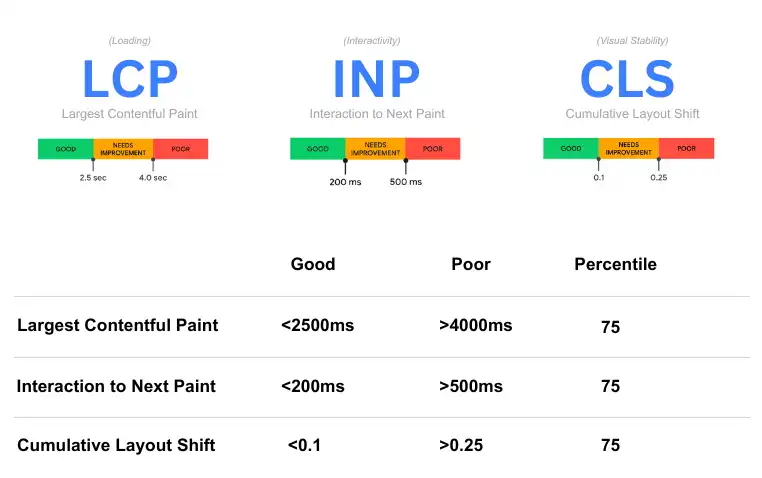
Core Web Vitals are Google’s way of measuring user experience on your website. These three metrics directly impact your search rankings and determine whether visitors stay or leave frustrated.
The three critical metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Measures loading performance. Target: 2.5 seconds or less. This tracks how long it takes for the main content on your page to load.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – Measures responsiveness. Target: 200 milliseconds or less. This tracks how quickly your website responds when someone clicks a button. Note that INP replaced First Input Delay (FID) in March 2024.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Measures visual stability. Target: 0.1 or less. This measures whether things on your page jump around while loading, which frustrates users.
How to improve these metrics: - Compress your images and use modern formats like WebP
- Implement lazy loading for images below the fold
- Minimize JavaScript execution time
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Specify image dimensions in your HTML
- Check your Core Web Vitals score using Google PageSpeed Insights for specific recommendations.
4. Improve Page Loading Speed
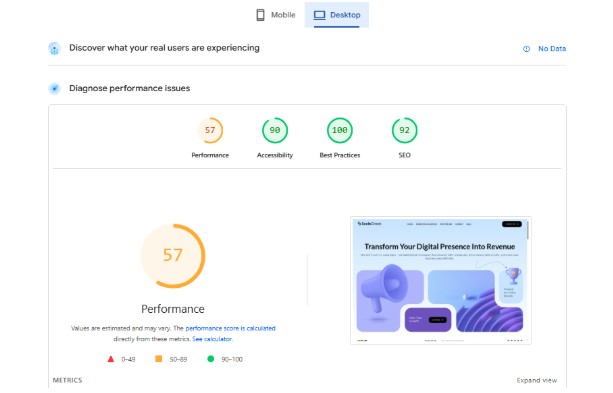
Nobody likes waiting for slow websites. Research shows that 40% of people abandon a website that takes more than three seconds to load. Page speed is a confirmed ranking factor that directly affects user experience.
Effective speed optimization strategies:
- Compress images before uploading them
- Remove plugins or features you don’t use
- Enable browser caching for returning visitors
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
- Choose a reliable, fast hosting provider
- Use a CDN to deliver content from servers closer to visitors
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to test your site speed and get specific recommendations for improvements.
5. Optimize XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is like a roadmap of your website that you give to search engines. It lists all your important pages and helps search engines find and index your content more efficiently.
What to include in your sitemap:
- All pages you want search engines to index
- Recent blog posts and updated content
- Important category and product pages
- Information about when pages were last updated
What NOT to include: - Duplicate pages or pages blocked by robots.txt
- Low-quality or thin content pages
- Thank you pages or
- checkout pages
- Pages with noindex tags
Once you create your sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console. This tells Google exactly where to find it and helps your content get indexed faster.
6. Check for Duplicate Content
Duplicate content happens when the same or very similar content appears on multiple pages. This confuses search engines-they don’t know which version to rank, so often none of them rank well.
Common duplicate content issues:
Your site is accessible at both http://yoursite.com and http://www.yoursite.com
Product pages with only minor variations
URL parameters creating multiple versions of the same page
How to fix duplicate content:
- Use canonical tags to tell search engines which version is the “original”
- Set up 301 redirects to send all versions to one main URL
- Choose either www or non-www and stick with it consistently
- Configure your URL parameters in Google Search Console
The goal is to have one clear version of each page that search engines can confidently index and rank.
7. Add Structured Data and Schema
Structured data (also called schema markup) is code you add to your website that helps search engines understand your content better. When you implement schema markup, you can get rich results in search those eye-catching listings with star ratings, images, prices, and other extra information.
Common types of schema to use:
- Organization schema: Shows your business name, logo, and contact information
- Product schema: Displays prices, availability, and ratings
- Article schema: Shows publish dates, authors, and featured images
- FAQ schema: Creates expandable question-and-answer boxes
- Review schema: Displays star ratings directly in search results
- Local business schema: Shows your address, hours, and phone number
Implementing schema markup can increase your click-through rates by 20-40% and helps your content appear in AI-generated search answers. Use Google’s Rich Results Test tool to verify your schema is implemented correctly.
8. Identify Crawl Errors
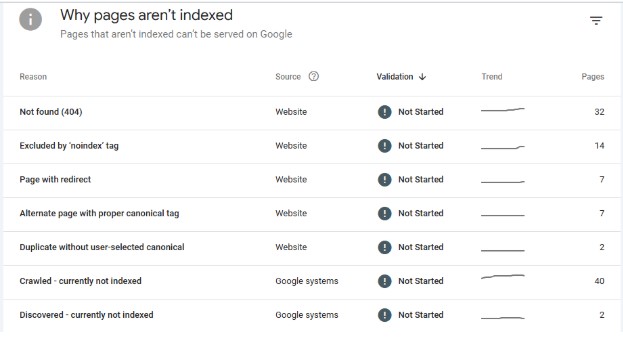
Crawl errors prevent search engines from accessing your pages. When Google’s bots try to visit a page and encounter an error, that page won’t be indexed-which means it won’t appear in search results.
Common crawl errors to watch for:
- 404 Errors: These happen when a page doesn’t exist anymore. Maybe you deleted it, moved it, or someone linked to a page that never existed.
- Server Errors (5xx): These indicate problems with your web server. They’re more serious because they can affect your entire site.
- Redirect Chains: This is when one URL redirects to another, which redirects to another. Each redirect slows things down and wastes crawl budget.
How to find and fix crawl errors:
- Check Google Search Console regularly for crawl error reports
- Use tools like Screaming Frog to identify issues
- Fix broken links or create 301 redirects to working pages
- Create a helpful custom 404 page
- Monitor your site regularly for new errors
9. Optimize Robot.txt File
The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which parts of your website they’re allowed to visit and which parts should stay private. It’s like having a “Do Not Enter” sign for certain areas of your site.
What to block in robots.txt:
- Admin and login pages
- Shopping cart and checkout pages
- Internal search results pages
- Duplicate content areas
10. Build a User-Friendly Architecture
Your website’s architecture refers to how your pages are organized and connected. A good structure helps both users and search engines navigate your site easily and find what they’re looking for quickly.
Key principles of good site architecture:
- Keep it flat: Visitors should be able to reach any page within 3-4 clicks from the homepage. The deeper a page is buried, the less important search engines think it is.
- Create logical categories: Group related content together in a way that makes sense.
- Use SEO-Friendly URLs: Your URLs should tell people what the page is about. “yoursite.com/blue-running-shoes” is much better than “yoursite.com/product?id=12345”
- Internal linking: Link to related pages within your content. This helps search engines discover more of your pages and keeps visitors engaged.
- Clear navigation menu: Your main menu should be consistent across all pages and include links to your most important sections.
11. Improve Navigation with Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are navigation links at the top of a page that show you where you are on the website. They look like: Home > Services> SEO> Running SEO.
Benefits of breadcrumbs:
- For users: Breadcrumbs show exactly where they are in your site structure and provide easy links to go back to broader category pages.
- For search engines: Breadcrumbs help Google understand your site hierarchy and relationships between pages. They also appear in search results, making your listing more professional.
Best practices: - Make each level clickable
- Keep the path logical and consistent
- Use schema markup so they appear properly in search results
- Use breadcrumbs to complement your main navigation, not replace it
Breadcrumbs are especially useful for large websites with many categories and subcategories.
Conclusion
Technical SEO is about making your website work better for both search engines and visitors. By following this technical SEO checklist, you’re building a solid foundation for all your marketing efforts. Start with the basics: mobile-friendliness, HTTPS security, and fast loading speed,s then gradually implement other items on this seo technical checklist. Regular audits using this expert technical seo checklist help catch issues before they impact rankings. Implement these comprehensive technical seo checklists today and watch your search performance improve over time.





